依據歐盟施行的個人資料保護法,我們致力於保護您的個人資料並提供您對個人資料的掌握。
按一下「全部接受」,代表您允許我們置放 Cookie 來提升您在本網站上的使用體驗、協助我們分析網站效能和使用狀況,以及讓我們投放相關聯的行銷內容。您可以在下方管理 Cookie 設定。 按一下「確認」即代表您同意採用目前的設定。
Research and Development
Skin Care
Plant exosomes are tiny vesicles secreted by plant cells, typically ranging in diameter from tens to hundreds of nanometers. These vesicles contain various biomolecules, including proteins, nucleic acids, lipids, and metabolites. The secretion of exosomes is often regulated by biotic or abiotic stimuli, such as pathogen infection, nutrient deficiency, or other physiological stresses.
In plant physiology, exosomes play multiple roles. Firstly, they are considered crucial mediators of intercellular communication. Exosomes can transport messages between different parts of the plant, regulating growth and development, stress responses, and disease resistance. Secondly, plant exosomes may be involved in sensing and responding to external environmental stimuli, facilitating interactions between plants and other organisms.
Compared to exosomes derived from mammals, plant-derived exosomes can be directly isolated from their fruits and tissues, significantly reducing the costs associated with raw materials and cultivation, thus offering advantages in mass production. Moreover, the potential applications of plant exosomes have been documented in the literature with various beneficial effects, such as antioxidative, anti-inflammatory, improvement of colitis, promotion of wound healing, serving as drug carriers, and even cancer treatment. Currently, three clinical trials related to plant exosomes are underway, indicating rapid advancements in this field over recent years.
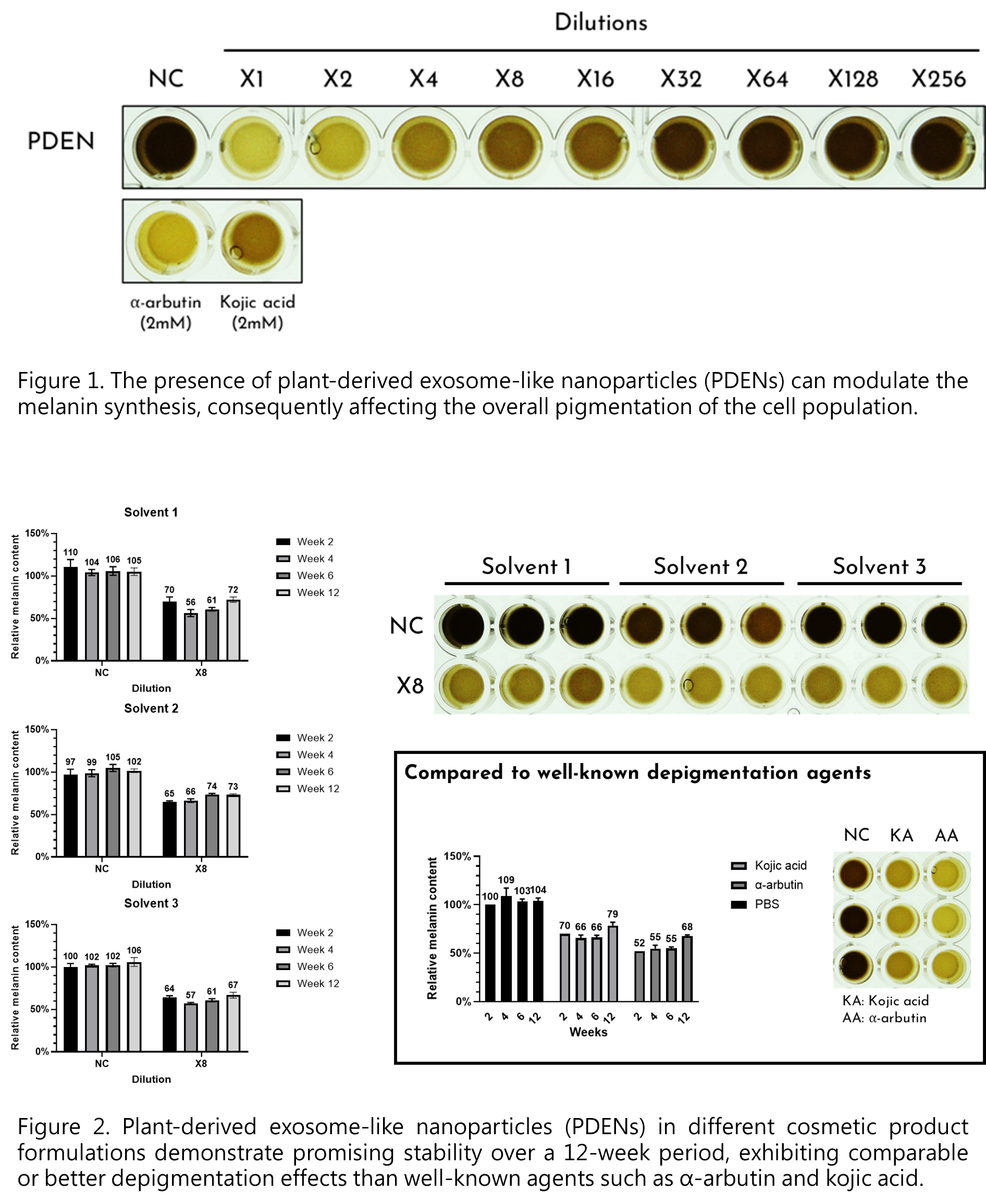
Stem Biotechnology Inc. is exploring the isolation of plant exosomes from common plants or crops and investigating their potential applications in cosmetics and skincare products. We have completed efficacy validation and cytotoxicity testing for a plant exosome raw material with whitening effects. Cell experiments have confirmed that its efficacy is comparable to commonly known whitening agents such as α-arbutin and kojic acid, effectively inhibiting melanin production. We are currently developing prototype whitening skincare products based on this raw material, with plans to enter mass production by the second half of 2024.
Kim, D. K., & Rhee, W. J. (2021). Antioxidative effects of carrot-derived nanovesicles in cardiomyoblast and neuroblastoma cells. Pharmaceutics, 13(8), 1203.
Kim, J., Li, S., Zhang, S., & Wang, J. (2022). Plant-derived exosome-like nanoparticles and their therapeutic activities. Asian journal of pharmaceutical sciences, 17(1), 53-69.
Nemati, M., Singh, B., Mir, R. A., Nemati, M., Babaei, A., Ahmadi, M., ... & Rezaie, J. (2022). Plant-derived extracellular vesicles: a novel nanomedicine approach with advantages and challenges. Cell Communication and Signaling, 20(1), 69.
Verma, M. L., Dhanya, B. S., Thakur, M., Jeslin, J., & Jana, A. K. (2021). Plant derived nanoparticles and their biotechnological applications. In Comprehensive analytical chemistry (Vol. 94, pp. 331-362). Elsevier.
Yang, C., Zhang, M., & Merlin, D. (2018). Advances in plant-derived edible nanoparticle-based lipid nano-drug delivery systems as therapeutic nanomedicines. Journal of Materials Chemistry B, 6(9), 1312-1321.
Yepes-Molina, L., Martínez-Ballesta, M. C., & Carvajal, M. (2020). Plant plasma membrane vesicles interaction with keratinocytes reveals their potential as carriers. Journal of advanced research, 23, 101-111.


